Post COVID-19
Platform for Sustainable
Health Management
Solutions
Health Management
Solutions
Economic Recovery
Green Recovery for low-carbon economy
The global economic shock due to the COVID-19 pandemic has been so profound that it represents the greatest contraction since the Second World War. (World Bank, 2020) The World Bank expects global GDP to grow by only 3.7% in 2021 which is below the pre-pandemic projections of 5.3 percent. Unlike the other major economic crises such as the Asian crisis of 1997 and global financial crisis in 2007-08, the economic recession caused by COVID-19 is different in its root cause. The root cause of the problem is not an economic event but a biological one. (IDB, 2020) Therefore, a green recovery that does not compromise the planet’s ecological and atmospheric stability is key for countries to achieve sustainable and resilient growth.
Green economic recovery has the potential to boost economic activity, reduce inequalities, enhance biodiversity conservation, and take effective climate action. The multiple crises, -the climate crisis, the nature crisis, and the pollution and waste crisis – are interconnected and must be addressed coherently to achieve sustainable development and growth after COVID-19. (UNEP, 2021) Green recovery is crucial for addressing the intertwined sustainable development goals of climate action (SDG 13), life below water (SDG 14), and life on land (SDG 15).
As unsustainable production and consumption caused crises leading to the COVID-19 outbreak, countries must find a way to deliver a green recovery which is vital for tackling these urgent challenges. Investments and capacity building for a smart and greener economy is important for a durable economy as digital transformation improves efficiency and low-carbon recovery enables a carbon-emissions reduction. In fact, many governments have included green recovery measures in recovery packages through grants, loans and tax reliefs that will be used for supporting green transport, circular economy and clean energy research, development, and deployment. (OECD, 2020)
Green economic recovery has the potential to boost economic activity, reduce inequalities, enhance biodiversity conservation, and take effective climate action. The multiple crises, -the climate crisis, the nature crisis, and the pollution and waste crisis – are interconnected and must be addressed coherently to achieve sustainable development and growth after COVID-19. (UNEP, 2021) Green recovery is crucial for addressing the intertwined sustainable development goals of climate action (SDG 13), life below water (SDG 14), and life on land (SDG 15).
As unsustainable production and consumption caused crises leading to the COVID-19 outbreak, countries must find a way to deliver a green recovery which is vital for tackling these urgent challenges. Investments and capacity building for a smart and greener economy is important for a durable economy as digital transformation improves efficiency and low-carbon recovery enables a carbon-emissions reduction. In fact, many governments have included green recovery measures in recovery packages through grants, loans and tax reliefs that will be used for supporting green transport, circular economy and clean energy research, development, and deployment. (OECD, 2020)

Regional and national stimulus packages for green recoveries (Source: ADB, 2020)
There are three factors that will determine the severity of economic loss: the extent of social distancing measures, the duration of such measures, and fiscal and monetary policy response. (JLL, 2020) Depending on the amplitude and duration of the shock affected by the 3 factors, the economy can display different kinds of recoveries such as V-shaped (quick recovery), U-shaped (prolonged drop followed by a quick recovery), W-shaped (relapse and recovery) and L- shaped recovery indicating permanent losses in productive capacity. (Sharma et al., 2021) With the resurgence of COVID-19 cases, a V-shaped recovery has been unattainable, and it is important for policymakers to make decisive decisions that will allow a V- or W-shaped recovery and prevent the economy from going into a prolonged crisis as shown in the L-shaped output curve. In the short run, if the economy is strong enough, injecting new money into households’ savings and easy credit for firms are effective policies which many governments have already implemented. (Sharma et al., 2021) In the case of Germany fiscal policies of temporary value-added tax cuts, support for SMEs, increased public spending on green investment, digital infrastructure, and healthcare were implemented and will remain supportive until a durable recovery is possible. (IMF, 2021)

4 different types of economic recoveries (Source: JLL, 2020)
Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Supported by the ongoing vaccination, the global recovery is expected to strengthen due to greater consumption, confidence, and improvement in trade in the long-term. (World Bank, 2020) It is important for governments to focus on green and innovative investments that will bring positive outcomes of low-carbon development, resource efficiency and social inclusion. Going green is simultaneously going smart as ICT development is a key strategy for energy-efficient production and lowering carbon emissions. Spending on renewable energy can create 2.5 times more jobs than fossil fuels which is another positive outcome for countries (McKinsey & Company, 2020) Such actions also reflect global public opinion. Two thirds of 28,000 respondents of a global survey agreed that governments should prioritize climate change in economic recovery. (McKinsey & Company, 2020)
The OECD illustrated four main categories of fiscal instruments countries can refer when making decisions.
The OECD illustrated four main categories of fiscal instruments countries can refer when making decisions.
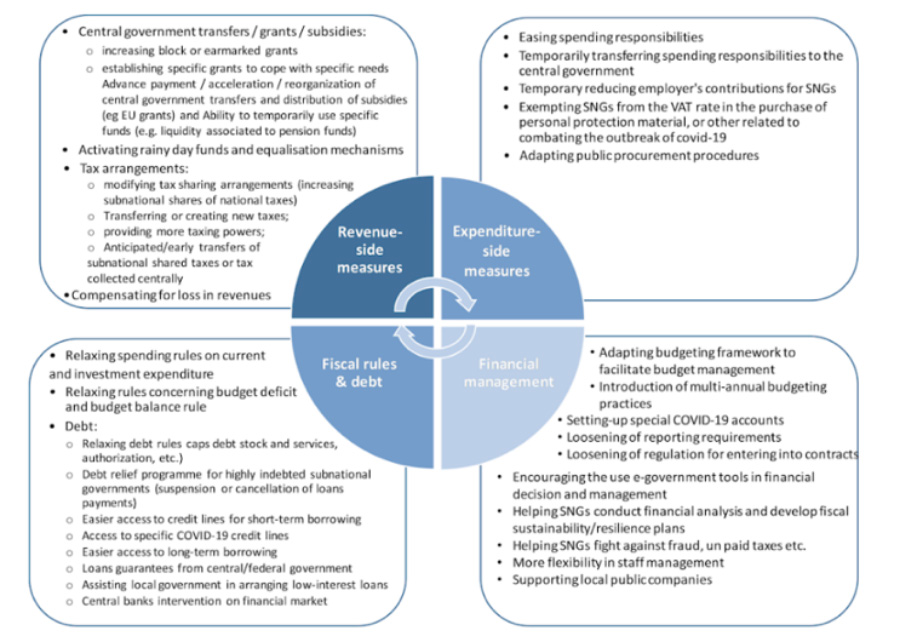
Four main categories of fiscal instruments (OECD, 2020)
Numerous central banks utilized monetary policy to further lower interest rates and provide liquidity to the economy and financial stability that can prevent permanent loss in productivity capacity demonstrated by the L-shaped output curve. Vast credit support is necessary especially for SMEs to recover from supply and demand shocks. However, expansionary monetary policy can lead to problems such as high inflation due to an overabundance of money.
Six prescriptions for green recovery
The WHO Director-General, Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, outlined 6 prescriptions for a healthy and green recovery at the World Health Assembly in 2020. (WHO, 2020) The WHO Manifesto presents the urgency and importance of the role of governments in constructing green economic recovery packages. The following is the 6 main themes governments must consider protecting lives, and the environment.
1) Protect and preserve the source of human health: Nature.
Through sustainable consumption and production, nature must be preserved to prevent emerging infectious diseases in humans. Reducing the risk of climate crisis is reducing the risk of economic crisis.
2) Invest in essential services, from water and sanitation to clean energy in healthcare facilities.
Investments in healthier environments for health protection, environmental regulation, and ensuring that health systems are climate resilient, are important to prevent future diseases and will offer some of the best returns for society.
3) Ensure a quick health energy transition
The price of renewable energy generation and storage continues to fall gradually, and renewable energy is becoming highly reliable and providing a greater number of safer and higher paid jobs. A rapid global transition to clean energy is vital.
4) Promote healthy, sustainable food systems
Conditions such as obesity and diabetes are among the largest risk factors for illness and death from COVID-19. Ending poverty, improving access to food and nutritious diets will save millions of lives, reduce disease risks, and reduce global GHGs.
5) Build healthy and livable cities
Over half of the world’s population lives in cities and are responsible for over 60% of both economic activity and greenhouse gas emissions. Investments in green transport, green building, and clean air towards sustainable and smart cities will enhance economic activity and quality of lives.
6) Stop using taxpayers’ money to fund pollution.
Ceasing fossil fuel subsidies will incentivize businesses to change from strategies that focus on fossil fuels to strategies oriented to renewable energy.
Data Collection and Monitoring

Environmental indicators for a green recovery
(Source: OECD report -Making the green recovery work for jobs, income and growth, 2020)
(Source: OECD report -Making the green recovery work for jobs, income and growth, 2020)
The following are websites where data and policies related to Post-COVID19- recovery can be found:
OECD Weekly Tracker of economic activity:
https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/en/themes/global-economy
https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/en/themes/global-economy
OECD best practice guidelines:
https://www.oecd.org/digital/publicationsdocuments/bestpracticesguidelines/
https://www.oecd.org/digital/publicationsdocuments/bestpracticesguidelines/
IMF Policy Tracker (responses to COVID-19) by country:
https://www.imf.org/en/Topics/imf-and-covid19/Policy-Responses-to-COVID-19t
https://www.imf.org/en/Topics/imf-and-covid19/Policy-Responses-to-COVID-19t
WHO Manifesto: Actionable for a healthy recovery from COVID-19
https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/actionables-for-a-healthy-recovery-from-covid-19
https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/actionables-for-a-healthy-recovery-from-covid-19
Bibliography
COVID-19 Global Real Estate Implications. (2020). Retrieved 16 April 2021, from
https://www.jll.co.kr/en/trends-and-insights/research/covid-19-global-real-estate-implications
https://www.jll.co.kr/en/trends-and-insights/research/covid-19-global-real-estate-implications
Germany’s Post-COVID-19 Recovery in Five Charts. (2021). Retrieved 16 April 2021, from
https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2021/01/15/na011921-germanys-post-covid19-recovery-in-five-charts
https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2021/01/15/na011921-germanys-post-covid19-recovery-in-five-charts
Greening the Post-COVID-19 Recovery. (2021). Retrieved 17 April 2021, from
https://www.adb.org/news/infographics/greening-post-covid-19-recovery
https://www.adb.org/news/infographics/greening-post-covid-19-recovery
Here’s how governments can drive a sustainable recovery from COVID-19. (2021). Retrieved 16 April 2021, from
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2021/02/government-economic-recovery-finance-pandemic-covid-19/
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2021/02/government-economic-recovery-finance-pandemic-covid-19/
IDB. (2020). Initial Conditions for Economic Recovery after COVID-19. Retrieved from
https://publications.iadb.org/publications/english/document/Initial-Conditions-for-Economic-Recovery-after-COVID-19-A-Logical-and-Quantitative-Framework-for-Latin-American-and-Caribbean-Countries.pdf
https://publications.iadb.org/publications/english/document/Initial-Conditions-for-Economic-Recovery-after-COVID-19-A-Logical-and-Quantitative-Framework-for-Latin-American-and-Caribbean-Countries.pdf
McKinsey & Company. (2020). How a post-pandemic stimulus can both create jobs and help the climate. McKinsey & Company. Retrieved from
https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/sustainability/our-insights/how-a-post-pandemic-stimulus-can-both-create-jobs-and-help-the-climate
https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/sustainability/our-insights/how-a-post-pandemic-stimulus-can-both-create-jobs-and-help-the-climate
Monetary policies, strategies, and the Covid-19 crisis - G20 Insights. (2020). Retrieved 17 April 2021, from
https://www.g20-insights.org/policy_briefs/monetary-policies-strategies-and-the-covid-19-crisis-2/
https://www.g20-insights.org/policy_briefs/monetary-policies-strategies-and-the-covid-19-crisis-2/
Multilateral action for a green post-COVID-19 recovery. (2021). Retrieved 16 April 2021, from
https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/speech/multilateral-action-green-post-covid-19-recovery
https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/speech/multilateral-action-green-post-covid-19-recovery
OECD. (2020). Making the green recovery work for jobs, income and growth. Retrieved from
https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/making-the-green-recovery-work-for-jobs-income-and-growth-a505f3e7/
https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/making-the-green-recovery-work-for-jobs-income-and-growth-a505f3e7/
OECD. (2020). The territorial impact of COVID-19: Managing the crisis across levels of government. OECD. Retrieved from
https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/the-territorial-impact-of-covid-19-managing-the-crisis-across-levels-of-government-d3e314e1/#section-d1e2545
https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/the-territorial-impact-of-covid-19-managing-the-crisis-across-levels-of-government-d3e314e1/#section-d1e2545
OECD. (2021). Strengthening the recovery: The need for speed. OECD. Retrieved from
https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/economics/oecd-economic-outlook/volume-2020/issue-2_34bfd999-en
https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/economics/oecd-economic-outlook/volume-2020/issue-2_34bfd999-en
Sharma, D., Bouchaud, J., Gualdi, S., Tarzia, M., & Zamponi, F. (2021). V–, U–, L– or W–shaped economic recovery after Covid-19: Insights from an Agent Based Model. PLOS ONE, 16(3), e0247823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247823
WHO Manifesto for a healthy recovery from COVID-19. (2020). Retrieved 17 April 2021, from
https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/who-manifesto-for-a-healthy-recovery-from-covid-19
https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/who-manifesto-for-a-healthy-recovery-from-covid-19
World Bank. (2020). Global Economic Prospects. Retrieved from
https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/global-economic-prospects
https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/global-economic-prospects
Appendix
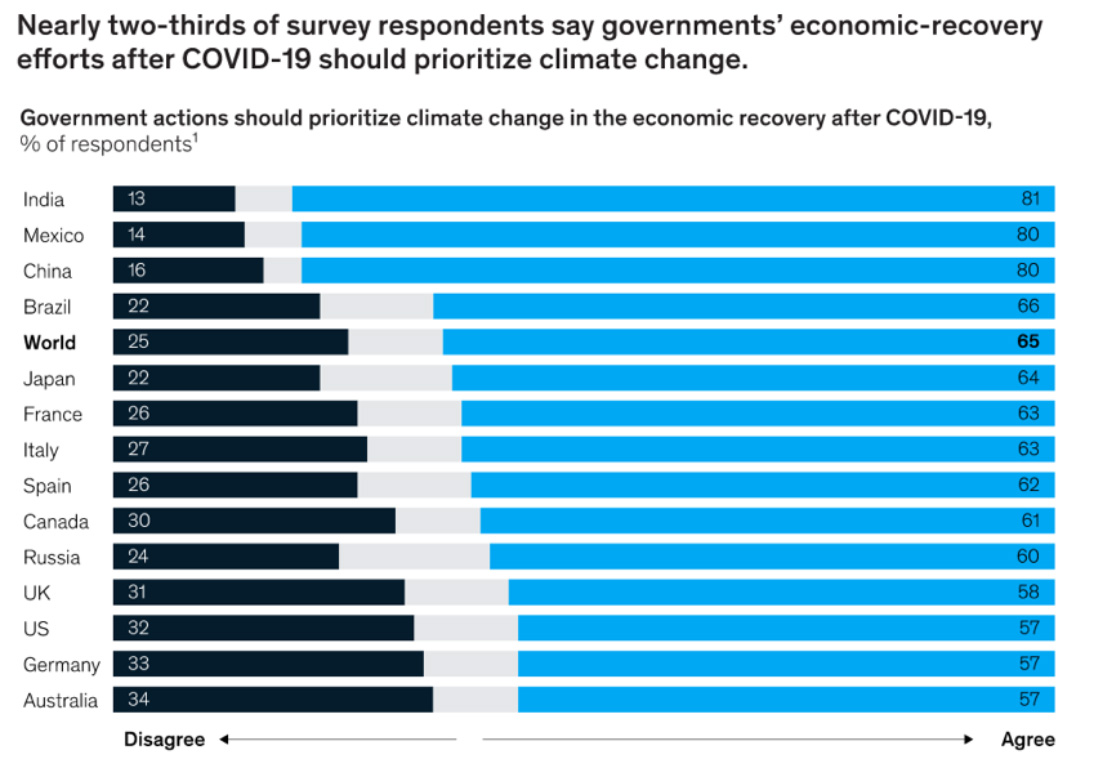
(Source: McKinsey & Company, 2020)


